Amazon EC2 with Suricata on AWS
Partner Solution Deployment Guide

September 2021
Pratik R. Mankad, AWS Strategic Accounts; Vaibhav Katkade, Amazon EC2 Product Management
Vinod Shukla, AWS Integration & Automation Team

| Refer to the GitHub repository to view source files, report bugs, submit feature ideas, and post feedback about this Partner Solution. To comment on the documentation, refer to Feedback. |
This Partner Solution was created by Amazon Web Services (AWS). Partner Solutions are automated reference deployments that help people deploy popular technologies on AWS according to AWS best practices. If you’re unfamiliar with AWS Partner Solutions, refer to the AWS Partner Solution General Information Guide.
Overview
This guide covers the information you need to deploy the Amazon EC2 with Suricata Partner Solution in the AWS Cloud.
This Amazon Web Services (AWS) Partner Solution provides instructions for deploying an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance with Suricata, an open-source tool for monitoring network traffic with Amazon VPC Traffic Mirroring.
The Partner Solution provides AWS CloudFormation templates for deploying Suricata on a single Amazon Linux 2 EC2 instance for limited scale deployments or behind a Network Load Balancer in an Auto Scaling group for highly available larger deployments.
| This Partner Solution does not configure VPC Traffic Mirroring. For information about configuring Traffic Mirroring to monitor your network traffic, see the Traffic Mirroring getting start guide. |
Costs and licenses
This Partner Solution installs Suricata on an Amazon Linux 2 EC2 instance. The Suricata source code is licensed under version 2 of the GNU General Public License.
There is no cost to use this Partner Solution, but you will be billed for any AWS services or resources that this Partner Solution deploys. For more information, refer to the AWS Partner Solution General Information Guide.
Architecture
Deploying this Partner Solution with default parameters builds the following Suricata on Amazon Linux 2 environment in the AWS Cloud.
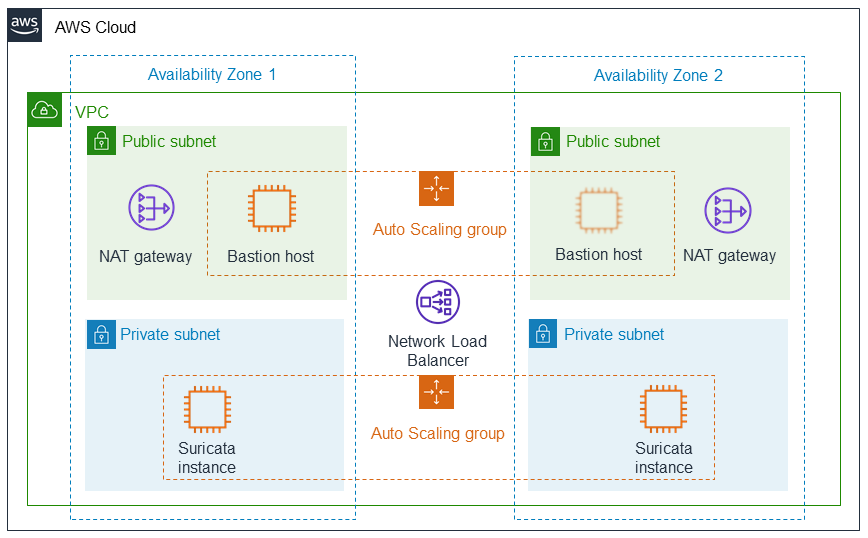
As shown in Figure 1, this Partner Solution sets up the following:
-
A highly available architecture that spans two Availability Zones.*
-
A virtual private cloud (VPC) configured with public and private subnets, according to AWS best practices, to provide you with your own virtual network on AWS.*
-
In the public subnets:
-
Managed network address translation (NAT) gateways to allow outbound internet access for resources in the private subnets.*
-
A Linux bastion host in an Auto Scaling group to allow inbound Secure Shell (SSH) access to Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances in public and private subnets.*
-
-
In the private subnets:
-
EC2 instances in an Auto Scaling group used for deploying across two Availability Zones, offering high availability.
-
A Network Load Balancer to balance traffic between the EC2 instances. For limited scale deployments, you can skip the Network Load Balancer setup and work directly with Suricata deployed on a single Amazon Linux 2 instance by choosing
TrafficMirrorTargetTypeasENIandNumTargetEC2Instancesas1.
-
* The template that deploys this Partner Solution into an existing VPC skips the components marked by asterisks and prompts you for your existing VPC configuration.
| This Partner Solution does not configure VPC Traffic Mirroring. For information about configuring Traffic Mirroring to monitor your network traffic, see the Traffic Mirroring getting start guide. |
Deployment options
This Partner Solution provides the following deployment options:
-
Deploy Suricata on Amazon Linux 2 into a new VPC. This option builds a new AWS environment that consists of the VPC, subnets, NAT gateways, security groups, bastion hosts, and other infrastructure components. It then deploys Suricata on Amazon Linux 2 into this new VPC.
-
Deploy Suricata on Amazon Linux 2 into an existing VPC. This option provisions Suricata on Amazon Linux 2 in your existing AWS infrastructure.
This Partner Solution provides separate templates for these options. It also lets you configure Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) blocks, instance types, and Suricata on Amazon Linux 2 settings.
Deployment steps
-
Sign in to your AWS account, and launch this Partner Solution, as described under Deployment options. The AWS CloudFormation console opens with a prepopulated template.
-
Choose the correct AWS Region, and then choose Next.
-
On the Create stack page, keep the default setting for the template URL, and then choose Next.
-
On the Specify stack details page, change the stack name if needed. Review the parameters for the template. Provide values for the parameters that require input. For all other parameters, review the default settings and customize them as necessary. When you finish reviewing and customizing the parameters, choose Next.
Unless you’re customizing the Partner Solution templates or are instructed otherwise in this guide’s Predeployment section, don’t change the default settings for the following parameters: QSS3BucketName,QSS3BucketRegion, andQSS3KeyPrefix. Changing the values of these parameters will modify code references that point to the Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket name and key prefix. For more information, refer to the AWS Partner Solutions Contributor’s Guide. -
On the Configure stack options page, you can specify tags (key-value pairs) for resources in your stack and set advanced options. When you finish, choose Next.
-
On the Review page, review and confirm the template settings. Under Capabilities, select all of the check boxes to acknowledge that the template creates AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) resources that might require the ability to automatically expand macros.
-
Choose Create stack. The stack takes about 10 minutes to deploy.
-
Monitor the stack’s status, and when the status is CREATE_COMPLETE, the Amazon EC2 with Suricata deployment is ready.
-
To view the created resources, choose the Outputs tab.
Postdeployment steps
Test the deployment
Perform the following steps to verify that Suricata is installed and running on the target instances.
-
Make a note of the TargetInstanceASG value shown in the Outputs tab.
-
Using either AWS CLI or the AWS Management Console, identify the IDs of the instances in the Auto Scaling group. For example, you can use the following CLI command to fetch the instance IDs.
aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --auto-scaling-group-name ${YOUR_ASG_NAME} --region ${DEPLOY_REGION} | grep -i instanceid | awk '{print $2}'Sample output:
"i-0c28001ae82907b0a", "i-0c425ea76fe462214", -
Using either AWS CLI or the AWS Management Console, connect to any of the instances in the output of the previous command and verify that Suricata is installed.
aws ssm start-session --target ${INSTANCE_ID} --region ${DEPLOY_REGION} # In the started session sudo su ec2-user # Verify Suricata version suricata build-info | head -1 # Verify Suricata service status systemctl status suricataSample output:
% aws ssm start-session --target ${INSTANCE_ID} --region ${DEPLOY_REGION} Starting session with SessionId: xxxx-yyyy-12345678abcd8888a sh-4.2$ sudo su ec2-user [ec2-user@ip-10-0-17-42 bin]$ suricata build-info | head -1 Suricata 6.0.3 [ec2-user@ip-10-0-17-42 bin]$ systemctl status suricata ● suricata.service - Suricata Intrusion Detection Service Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/suricata.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Thu 2021-07-22 05:17:33 UTC; 24h ago Docs: man:suricata(1) Main PID: 6879 (Suricata-Main) CGroup: /system.slice/suricata.service └─6879 /sbin/suricata -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml --pidfile /var/run/suricata.pid -i eth0 --user suricata Jul 22 05:17:33 ip-10-0-17-42.us-west-2.compute.internal systemd[1]: Starting Suricata Intrusion Detection Service... Jul 22 05:17:33 ip-10-0-17-42.us-west-2.compute.internal systemd[1]: Started Suricata Intrusion Detection Service. ...output truncated...
Troubleshooting
For troubleshooting common Partner Solution issues, refer to the AWS Partner Solution General Information Guide and Troubleshooting CloudFormation.
Customer responsibility
After you deploy a Partner Solution, confirm that your resources and services are updated and configured—including any required patches—to meet your security and other needs. For more information, refer to the Shared Responsibility Model.
Feedback
To submit feature ideas and report bugs, use the Issues section of the GitHub repository for this Partner Solution. To submit code, refer to the Partner Solution Contributor’s Guide. To submit feedback on this deployment guide, use the following GitHub links:
Notices
This document is provided for informational purposes only. It represents current AWS product offerings and practices as of the date of issue of this document, which are subject to change without notice. Customers are responsible for making their own independent assessment of the information in this document and any use of AWS products or services, each of which is provided "as is" without warranty of any kind, whether expressed or implied. This document does not create any warranties, representations, contractual commitments, conditions, or assurances from AWS, its affiliates, suppliers, or licensors. The responsibilities and liabilities of AWS to its customers are controlled by AWS agreements, and this document is not part of, nor does it modify, any agreement between AWS and its customers.
The software included with this paper is licensed under the Apache License, version 2.0 (the "License"). You may not use this file except in compliance with the License. A copy of the License is located at https://aws.amazon.com/apache2.0/ or in the accompanying "license" file. This code is distributed on an "as is" basis, without warranties or conditions of any kind, either expressed or implied. Refer to the License for specific language governing permissions and limitations.