Amazon Virtual Private Cloud on AWS
Partner Solution Deployment Guide

September 2022
Santiago Cardenas & Troy Lindsay, AWS Integration & Automation team

| Refer to the GitHub repository to view source files, report bugs, submit feature ideas, and post feedback about this Partner Solution. To comment on the documentation, refer to Feedback. |
This Partner Solution was created by Amazon Web Services (AWS). Partner Solutions are automated reference deployments that help people deploy popular technologies on AWS according to AWS best practices. If you’re unfamiliar with AWS Partner Solutions, refer to the AWS Partner Solution General Information Guide.
Overview
This guide covers the information you need to deploy the Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) Quick Start in the AWS Cloud.
Costs and licenses
There is no cost to use this Quick Start, but you will be billed for any AWS services or resources that this Quick Start deploys. For more information, refer to the AWS Quick Start General Information Guide.
There are no licensing requirements for this Quick Start.
Architecture
Deploying this Quick Start with default parameters builds the following Amazon VPC environment in the AWS Cloud.
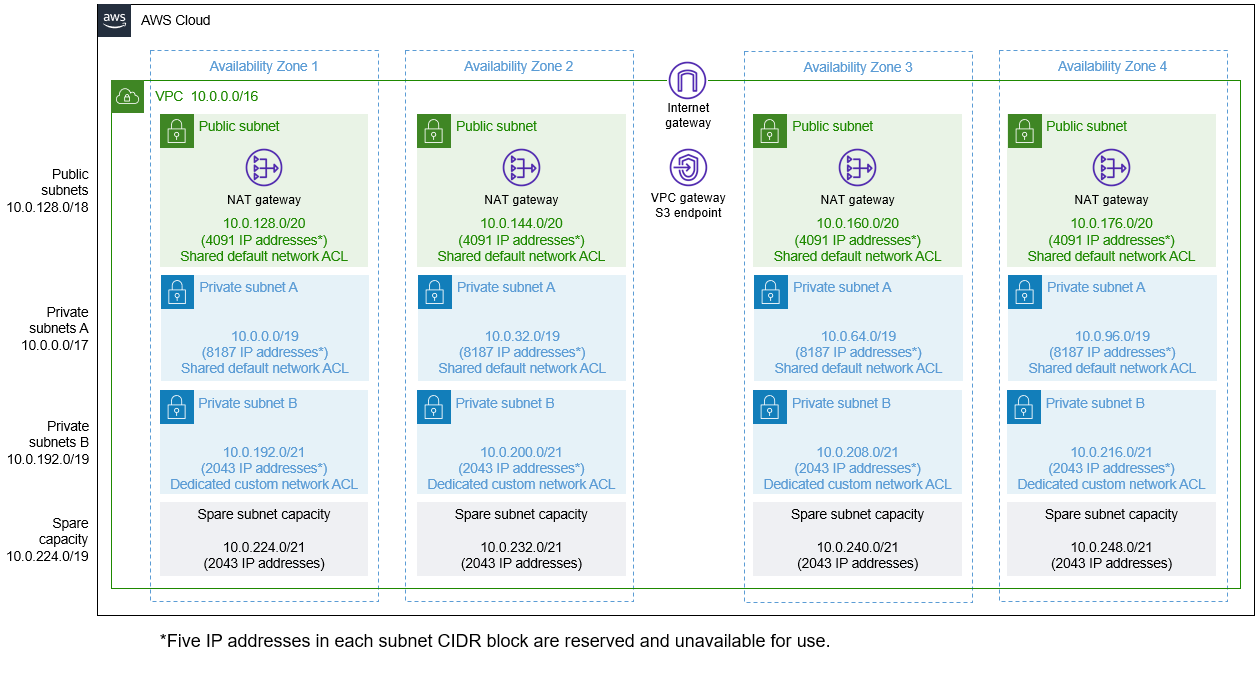
As shown in Figure 1, this Quick Start sets up the following:
-
A highly available architecture that spans two to four Availability Zones.
-
A virtual private cloud (VPC) configured with public and private subnets, according to AWS best practices, to provide you with your own virtual network on AWS. The VPC provides Domain Name System (DNS) resolution.
-
In the public subnets:
-
Managed network address translation (NAT) gateways to allow outbound internet access for resources in the private subnets.
-
Dedicated custom network access control lists (ACLs) for each Availability Zone.
-
A single routing table (not shown) because the public subnets all use the same internet gateway as the sole route to communicate with the internet.
-
-
In the private subnets:
-
Dedicated custom network ACLs for each Availability Zone.
-
An independent routing table (not shown) for each private subnet configured to control the flow of traffic within and outside the VPC.
-
Spare capacity for adding subnets to support your environment as it grows.
-
-
A VPC gateway endpoint for Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3). This endpoint provides a secure, reliable connection to Amazon S3 without requiring an internet gateway, NAT gateway, or virtual private gateway. The endpoint uses the default endpoint policy, which gives any user or service within the VPC full access to Amazon S3 resources. This policy supplements any IAM user policies or S3 bucket policies that you may have in place. With this endpoint, you can access S3 resources from within the VPC created by the Quick Start. This endpoint is valid only for the AWS Region in which you launch the Quick Start.
Related Amazon VPC documentation:
| Default subnet sizes are based on a typical deployment. You can reconfigure the sizes, as discussed in the Predeployment steps section. |
Deployment options
This Quick Start provides one deployment option:
-
Deploy a new Amazon VPC environment. This environment consists of a VPC, subnets, NAT gateways, and other infrastructure components.
Predeployment steps
In this Quick Start, the default sizing of CIDR blocks used in the subnets is based on a typical deployment, where private subnets would have roughly double the number of instances found in public subnets. You can use the CIDR block parameters to resize the CIDR scopes to meet your architectural needs.
In the default subnet allocation, the VPC is divided into subnet types and then further segmented by Availability Zone, as illustrated in Figure 1. The Quick Start provides default CIDR block sizes to maximize capacity, as listed in Table 1:
| VPC | 10.0.0.0/16 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Private subnets A |
10.0.0.0/17 |
||||||||
|
|||||||||
Public subnets |
10.0.128.0/18 |
||||||||
|
|||||||||
Private subnets B with dedicated custom network ACL |
10.0.192.0/19 |
||||||||
|
|||||||||
Spare subnet capacity |
10.0.224.0/19 |
||||||||
|
In some situations, you may want to separate the CIDR scopes by dividing the VPC into Availability Zones and then into subnet types. The recommended CIDR blocks to maximize capacity for this scenario are listed in Table 2:
| VPC | 10.0.0.0/16 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Availability Zone 1 |
10.0.0.0/18 |
||||||||
|
|||||||||
Availability Zone 2 |
10.0.64.0/18 |
||||||||
|
|||||||||
Availability Zone 3 |
10.0.128.0/18 |
||||||||
|
|||||||||
Availability Zone 4 |
10.0.192.0/18 |
||||||||
|
For more information, refer to Subnet sizing.
Deployment steps
-
Sign in to your AWS account, and launch this Partner Solution, as described under Deployment options. The AWS CloudFormation console opens with a prepopulated template.
-
Choose the correct AWS Region, and then choose Next.
-
On the Create stack page, keep the default setting for the template URL, and then choose Next.
-
On the Specify stack details page, change the stack name if needed. Review the parameters for the template. Provide values for the parameters that require input. For all other parameters, review the default settings and customize them as necessary. When you finish reviewing and customizing the parameters, choose Next.
Unless you’re customizing the Partner Solution templates or are instructed otherwise in this guide’s Predeployment section, don’t change the default settings for the following parameters: QSS3BucketName,QSS3BucketRegion, andQSS3KeyPrefix. Changing the values of these parameters will modify code references that point to the Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket name and key prefix. For more information, refer to the AWS Partner Solutions Contributor’s Guide. -
On the Configure stack options page, you can specify tags (key-value pairs) for resources in your stack and set advanced options. When you finish, choose Next.
-
On the Review page, review and confirm the template settings. Under Capabilities, select all of the check boxes to acknowledge that the template creates AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) resources that might require the ability to automatically expand macros.
-
Choose Create stack. The stack takes about 5 minutes to deploy.
-
Monitor the stack’s status, and when the status is CREATE_COMPLETE, the Amazon Virtual Private Cloud deployment is ready.
-
To view the created resources, choose the Outputs tab.
Postdeployment steps
After you use this Quick Start to build your Amazon VPC environment, you can deploy additional Quick Starts or deploy your own applications on top of this AWS infrastructure. If you extend your AWS environment with additional AWS Quick Starts for trial or production use, choose the option to deploy the Quick Start into an existing VPC where that option is available.
If you deploy additional private subnets with dedicated network ACLs, review the configuration and adjust it accordingly. By default, the custom ACLs are configured to allow all inbound and outbound traffic to flow to facilitate the deployment of additional infrastructure. For more information, refer to the Amazon VPC documentation:
Troubleshooting
For troubleshooting common Quick Start issues, refer to the AWS Quick Start General Information Guide and Troubleshooting CloudFormation.
Customer responsibility
After you deploy a Partner Solution, confirm that your resources and services are updated and configured—including any required patches—to meet your security and other needs. For more information, refer to the Shared Responsibility Model.
Feedback
To submit feature ideas and report bugs, use the Issues section of the GitHub repository for this Partner Solution. To submit code, refer to the Partner Solution Contributor’s Guide. To submit feedback on this deployment guide, use the following GitHub links:
Notices
This document is provided for informational purposes only. It represents current AWS product offerings and practices as of the date of issue of this document, which are subject to change without notice. Customers are responsible for making their own independent assessment of the information in this document and any use of AWS products or services, each of which is provided "as is" without warranty of any kind, whether expressed or implied. This document does not create any warranties, representations, contractual commitments, conditions, or assurances from AWS, its affiliates, suppliers, or licensors. The responsibilities and liabilities of AWS to its customers are controlled by AWS agreements, and this document is not part of, nor does it modify, any agreement between AWS and its customers.
The software included with this paper is licensed under the Apache License, version 2.0 (the "License"). You may not use this file except in compliance with the License. A copy of the License is located at https://aws.amazon.com/apache2.0/ or in the accompanying "license" file. This code is distributed on an "as is" basis, without warranties or conditions of any kind, either expressed or implied. Refer to the License for specific language governing permissions and limitations.