Internet Information Services on AWS
Partner Solution Deployment Guide

March 2022
Aaron Lima, Jonthan Lozano, and Syed Ahmad, AWS

| Refer to the GitHub repository to view source files, report bugs, submit feature ideas, and post feedback about this Partner Solution. To comment on the documentation, refer to Feedback. |
This Partner Solution was created by Amazon Web Services (AWS). Partner Solutions are automated reference deployments that help people deploy popular technologies on AWS according to AWS best practices. If you’re unfamiliar with AWS Partner Solutions, refer to the AWS Partner Solution General Information Guide.
Overview
This Partner Solution deploys Internet Information Services on the AWS Cloud. If you are unfamiliar with AWS Partner Solutions, refer to the AWS Partner Solution General Information Guide.
Costs and licenses
There is no cost to use this Partner Solution, but you will be billed for any AWS services or resources that this Partner Solution deploys. For more information, refer to the AWS Partner Solution General Information Guide.
This Partner Solution launches with Windows Server 2019 Core AMI. It includes the license for Windows Server, which is updated on a regular basis with the latest service pack. To modify the Windows Server version, edit the ImageId parameter in /templates/asg-lch.template.yaml. For a list of Windows images, run the following command from the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI):
aws ssm get-parameters-by-path --path "/aws/service/ami-windows-latest" --region us-east-1| For more information, see Microsoft Licensing on AWS. |
Architecture
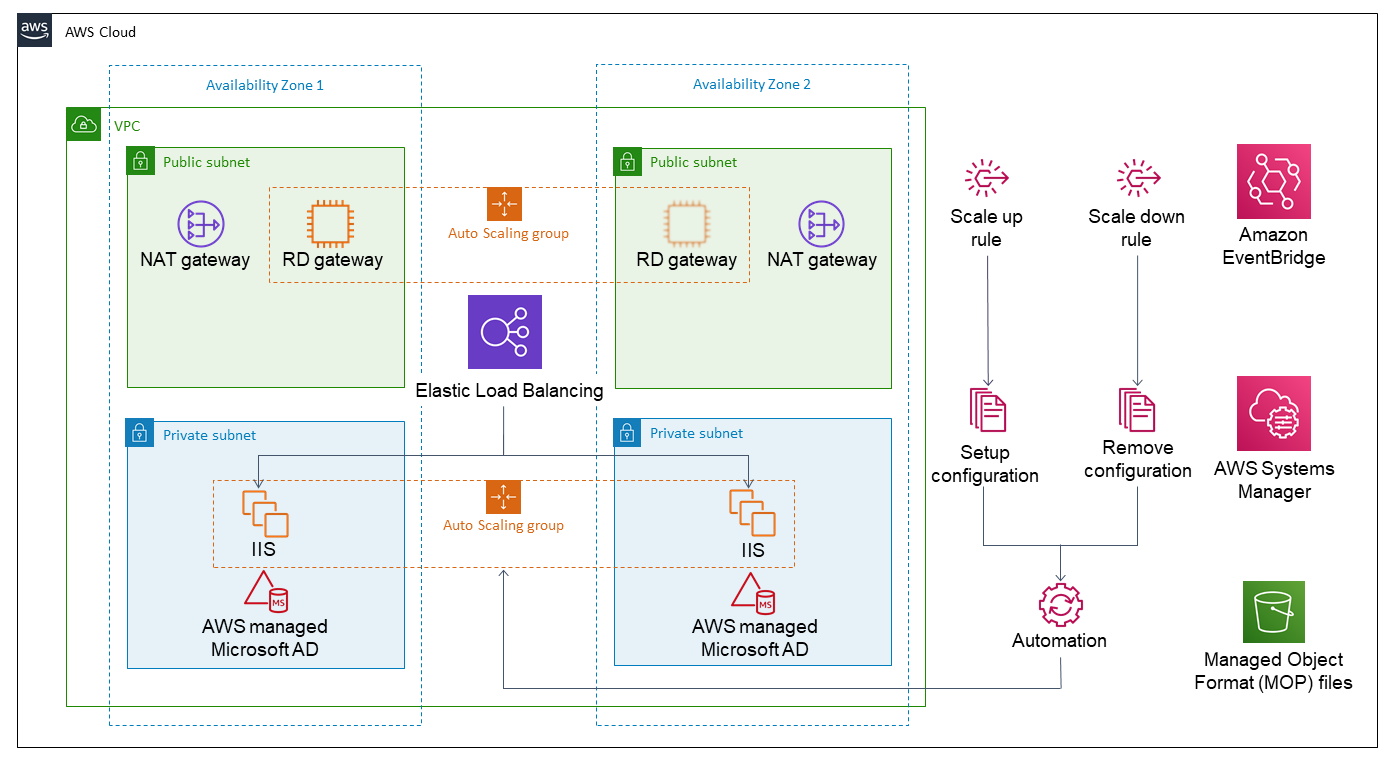
Deploying this Partner Solution for a new virtual private cloud (VPC) with default parameters builds the following IIS environment in the AWS Cloud.
As shown in Figure 1, the Partner Solution sets up the following:
-
A highly available architecture that spans two Availability Zones.*
-
A VPC configured with public and private subnets according to AWS best practices, to provide you with your own virtual network on AWS.*
-
In the public subnets:
-
Managed network address translation (NAT) gateways to allow internet access for resources in the private subnets.*
-
Elastic Load Balancers to distribute traffic across EC2 instances.
-
Remote Desktop (RD) gateways in an Auto Scaling group.
-
-
In the private subnets:
-
Auto Scaling group of EC2 instances into which Microsoft IIS is deployed.
-
AWS Directory Service for Microsoft Active Directory.
-
-
Amazon EventBridge, providing the rules that trigger automation routines in response to Auto Scaling events.
-
AWS Systems Manager to store automation documents.
-
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles.
-
Security groups to control traffic to your EC2 instances.
-
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket for storing MOP files.
*The template that deploys the Partner Solution into an existing VPC skips the components marked by asterisks and prompts you for your existing VPC configuration.
Deployment options
This Partner Solution provides the following deployment options:
-
Deploy IIS into a new VPC. This option builds a new AWS environment that consists of the VPC, subnets, NAT gateways, security groups, bastion hosts, and other infrastructure components. It then deploys IIS into this new VPC.
-
Deploy IIS into an existing VPC. This option provisions IIS in your existing AWS infrastructure.
This Partner Solution provides separate templates for these options. It also lets you configure Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) blocks, instance types, and IIS settings.
Predeployment steps
Deployment steps
-
Sign in to your AWS account, and launch this Partner Solution, as described under Deployment options. The AWS CloudFormation console opens with a prepopulated template.
-
Choose the correct AWS Region, and then choose Next.
-
On the Create stack page, keep the default setting for the template URL, and then choose Next.
-
On the Specify stack details page, change the stack name if needed. Review the parameters for the template. Provide values for the parameters that require input. For all other parameters, review the default settings and customize them as necessary. When you finish reviewing and customizing the parameters, choose Next.
Unless you’re customizing the Partner Solution templates or are instructed otherwise in this guide’s Predeployment section, don’t change the default settings for the following parameters: QSS3BucketName,QSS3BucketRegion, andQSS3KeyPrefix. Changing the values of these parameters will modify code references that point to the Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket name and key prefix. For more information, refer to the AWS Partner Solutions Contributor’s Guide. -
On the Configure stack options page, you can specify tags (key-value pairs) for resources in your stack and set advanced options. When you finish, choose Next.
-
On the Review page, review and confirm the template settings. Under Capabilities, select all of the check boxes to acknowledge that the template creates AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) resources that might require the ability to automatically expand macros.
-
Choose Create stack. The stack takes about 1 hour to deploy.
-
Monitor the stack’s status, and when the status is CREATE_COMPLETE, the Internet Information Services deployment is ready.
-
To view the created resources, choose the Outputs tab.
Post-deployment steps
Run Windows Updates
In order to ensure the deployed servers' operating systems and installed applications have the latest Microsoft updates, run Windows Update on each server.
-
Create an RDP session from the Remote Desktop Gateway server to each deployed server.
-
Open the Settings application.
-
Open Update & Security.
-
Click Check for updates.
-
Install any updates and reboot if necessary.
Testing the deployment
To test the deployment, ensure that your IP address is entered in the WebAccessCIDR parameter. If it is, you can enter the URL of your Elastic Load Balancer (part of the output of the WebAutoScaleStack) into a web browser. The window shown in Figure 2 is displayed.
| If you are unable to connect to the test page, review the security groups for the Elastic Load Balancers and verify that the CIDR ranges are correct. |
Using AWS Systems Manager Agent
This Partner Solution deploys AWS Systems Manager Agent (SSM Agent) on all EC2 instances. With SSM Agent, you can use the Windows remote desktop protocol (RDP) to connect to EC2 instances without the need for an RDP bastion host or opening inbound port 3389 with Session Manager. This section explains the requirements for using this feature and how to connect to an EC2 instance of Windows Server using RDP.
See the following sites for more information about these AWS services and software:
Prerequisites
-
AWS Command Line Interface must be installed on your desktop.
-
AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) must be configured with security credentials for your AWS account.
-
Session Manager plugin for AWS CLI must be installed.
-
SSM Agent must be installed on EC2 instances.*
-
Instance role attached allowing access to Systems Manager API.*
*These prerequisites are completed automatically as part of the Partner Solution deployment.
Connecting to a Windows instance with RDP
-
Start a port forwarding session.
-
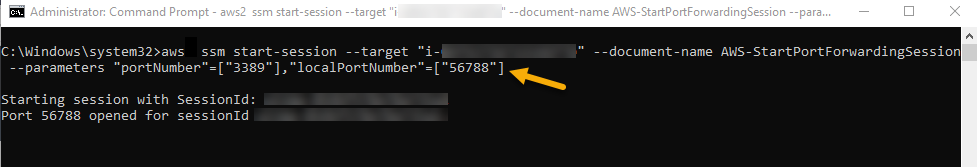
Navigate to the EC2 Console, and note the instance ID (for example, "i-1234567890abcdef0").
-
Run the following command in the AWS CLI by providing your target instance ID after the --target parameter. (See Figure 3.)
-
aws ssm start-session --target "<your-instance-id>" --document-name AWS-StartPortForwardingSession --parameters "portNumber"=["3389"],"localPortNumber"=["56788"]-
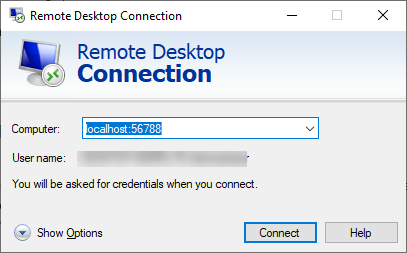
When the session is established, open the Remote Desktop application, and enter localhost:56788 (or any port number that’s not currently in use.)
-
Choose Connect.
-
When the client prompts you for credentials, enter the appropriate password to log in.
-
When you finish, end your Remote Desktop session and disconnect.
Post-deployment steps
If you want to modify this Partner Solution see the automation-parts.template.yaml template. This AWS Cloudformation template uploads the MOF files and creates the automation documents that are triggered by the Auto Scaling group’s lifecycle hooks.
The following code block demonstrates a step in the AWS Systems Manager automation document. These steps under the main step section can be modified to support your own automation steps and configuration.
- name: "setNameTag"
action: aws:runCommand
onFailure: "step:abandonHookAction"
inputs:
DocumentName: AWS-RunPowerShellScript
InstanceIds:
- "{{InstanceId}}"
CloudWatchOutputConfig:
CloudWatchOutputEnabled: "true"
CloudWatchLogGroupName: "/QuickStart/SetupConfiguration"
Parameters:
commands:
- |
Import-Module AWSPowerShell
$instanceid = (Invoke-RestMethod -Method Get -Uri http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/instance-id)
New-EC2Tag -Resource $instanceId -Tag @{Key="Name";Value=$env:COMPUTERNAME}| For more information about automation documents, see Systems Manager Automation actions reference. |
Best practices for using IIS on AWS
For best practices to help you get the intended results from running Windows on Amazon EC2, see the following sites:
Troubleshooting
For troubleshooting common Partner Solution issues, refer to the AWS Partner Solution General Information Guide.
For any other issues see Troubleshooting AWS CloudFormation. For issues with AWS Systems Manager see Troubleshooting Systems Manager Run Command and Troubleshooting Systems Manager Automation.
Customer responsibility
After you deploy a Partner Solution, confirm that your resources and services are updated and configured—including any required patches—to meet your security and other needs. For more information, refer to the Shared Responsibility Model.
Feedback
To submit feature ideas and report bugs, use the Issues section of the GitHub repository for this Partner Solution. To submit code, refer to the Partner Solution Contributor’s Guide. To submit feedback on this deployment guide, use the following GitHub links:
Notices
This document is provided for informational purposes only. It represents current AWS product offerings and practices as of the date of issue of this document, which are subject to change without notice. Customers are responsible for making their own independent assessment of the information in this document and any use of AWS products or services, each of which is provided "as is" without warranty of any kind, whether expressed or implied. This document does not create any warranties, representations, contractual commitments, conditions, or assurances from AWS, its affiliates, suppliers, or licensors. The responsibilities and liabilities of AWS to its customers are controlled by AWS agreements, and this document is not part of, nor does it modify, any agreement between AWS and its customers.
The software included with this paper is licensed under the Apache License, version 2.0 (the "License"). You may not use this file except in compliance with the License. A copy of the License is located at https://aws.amazon.com/apache2.0/ or in the accompanying "license" file. This code is distributed on an "as is" basis, without warranties or conditions of any kind, either expressed or implied. Refer to the License for specific language governing permissions and limitations.