Multi-Cluster centralized hub-spoke topology¶
This tutorial guides you through deploying an Amazon EKS cluster with addons configured via ArgoCD in a Multi-Cluster Hub-Spoke topology, employing the GitOps Bridge Pattern.
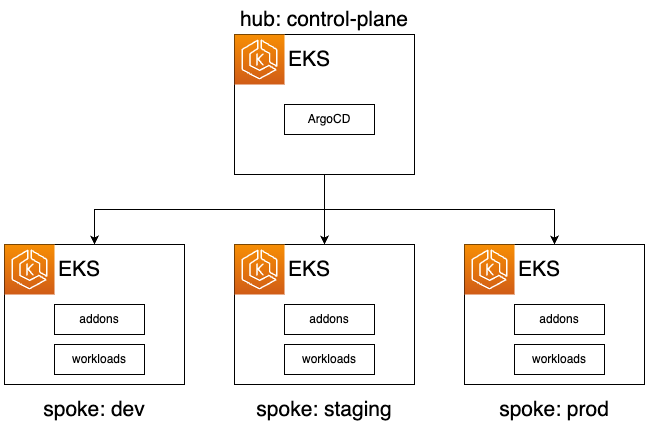
This example deploys ArgoCD on the Hub cluster (i.e. management/control-plane cluster). The spoke clusters are registered as remote clusters in the Hub Cluster's ArgoCD The ArgoCD on the Hub Cluster deploys addons and workloads to the spoke clusters
Each spoke cluster gets deployed an app of apps ArgoCD Application with the name workloads-${env}
Prerequisites¶
Before you begin, make sure you have the following command line tools installed:
- git
- terraform
- kubectl
- argocd
(Optional) Fork the GitOps git repositories¶
See the appendix section Fork GitOps Repositories for more info on the terraform variables to override.
Deploy the Hub EKS Cluster¶
Change directory to hub
Initialize Terraform and deploy the EKS cluster:
terraform init
terraform apply -target="module.vpc" -auto-approve
terraform apply -target="module.eks" -auto-approve
terraform apply -auto-approve
To retrieve kubectl config, execute the terraform output command:
The expected output will have two lines you run in your terminal
export KUBECONFIG="/tmp/hub-spoke"
aws eks --region us-west-2 update-kubeconfig --name getting-started-gitops --alias hub
The first line sets the
KUBECONFIGenvironment variable to a temporary file that includes the cluster name. The second line uses theawsCLI to populate that temporary file with thekubectlconfiguration. This approach offers the advantage of not altering your existingkubectlcontext, allowing you to work in other terminal windows without interference.
Deploy ArgoCD Apps of ApplicationSets for Addons¶
This command verifies the initial ArgoCD installation, ArgoCD will be re-configured when the addons are deployed and configured from git.
This command creates the application set manifest to deploy the addons. The application sets defined here will then deploy addons to any spoke clusters provisioned later using TerraformMonitor GitOps Progress for Addons on Hub EKS Cluster¶
Wait until all the ArgoCD applications' HEALTH STATUS is Healthy.
Use Ctrl+C or Cmd+C to exit the watch command. ArgoCD Applications
can take a couple of minutes in order to achieve the Healthy status.
The expected output should look like the following:
NAME SYNC STATUS HEALTH STATUS
addon-in-cluster-argo-cd Synced Healthy
addon-in-cluster-aws-load-balancer-controller Synced Healthy
addon-in-cluster-metrics-server Synced Healthy
cluster-addons Synced Healthy
(Optional) Access ArgoCD¶
Access to the ArgoCD's UI is completely optional, if you want to do it, run the commands shown in the Terraform output as the example below:
The expected output should contain the kubectl config followed by kubectl command to retrieve
the URL, username, password to login into ArgoCD UI or CLI.
echo "ArgoCD Username: admin"
echo "ArgoCD Password: $(kubectl --context hub get secrets argocd-initial-admin-secret -n argocd --template="{{index .data.password | base64decode}}")"
echo "ArgoCD URL: https://$(kubectl --context hub get svc -n argocd argo-cd-argocd-server -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].hostname}')"
Deploy the Spoke EKS Cluster¶
Use the deploy.sh script to create terraform workspace, initialize Terraform, and deploy the EKS clusters:
You may want to create few spoke environments to validate multi-cluster hub spoke to avoid quota limits
Each environment uses a Terraform workspace
To retrieve kubectl config, execute the terraform output command:
Verify ArgoCD Cluster Secret for Spokes have the correct IAM Role to be assume by Hub Cluster¶
for i in dev staging prod ; do echo $i && kubectl --context hub get secret -n argocd spoke-$i --template='{{index .data.config | base64decode}}' ; done
The output have a section awsAuthConfig with the clusterName and the roleARN that has write access to the spoke cluster
{
"tlsClientConfig": {
"insecure": false,
"caData" : "LS0tL...."
},
"awsAuthConfig" : {
"clusterName": "hub-spoke-dev",
"roleARN": "arn:aws:iam::0123456789:role/hub-spoke-dev-argocd-spoke"
}
}
Verify the Addons on Spoke Clusters¶
The addons on the spoke clusters are deployed using the Application Sets created on the EKS Hub Cluster. Verify that the addons are ready:
Deploy the sample application to EKS Spoke Clusters¶
This command will deploy the application using kubectl to all clusters connected to the hub cluster, using the manifest files in ./hub/bootstrap/workloads.yaml.
Monitor GitOps Progress for Workloads from Hub Cluster (run on Hub Cluster context)¶
Watch until all the Workloads ArgoCD Applications are Healthy
Wait until the ArgoCD Applications HEALTH STATUS is Healthy. Crl+C to exit the watch command
Verify the Application¶
Verify that the application configuration is present and the pod is running:
Container Metrics¶
Check the application's CPU and memory metrics:
Destroy the Spoke EKS Clusters¶
To tear down all the resources and the EKS cluster, run the following command:
Destroy the Hub EKS Clusters¶
To tear down all the resources and the EKS cluster, run the following command: Destroy Hub Clusters
Appendix¶
Fork GitOps Repositories¶
To modify the values.yaml file or the helm chart version for addons, you'll need to fork the repository aws-samples/eks-blueprints-add-ons.
After forking, update the following environment variables to point to your forks, replacing the default values.